Quantum theory is a theory needed to describe physics on a microscopic scale, such as on the scale of atoms, molecules,electrons, protons, etc
where as Classical theories deals with
Newton – Mechanical motion of objects (F = ma)
Maxwell – Light treated as a wave
but NEITHER OF THESE THEORIES QUITE WORK FOR
ATOMS, MOLECULES, ETC.
- This name quantum mechanics derives from the observation that some physical quantities can change only in discrete amounts where Quanta is the Latin word.
- Wave-particle duality principle is an example of the principle of complementarity in quantum physics.
- At the macroscopic scale we are used to two broad types of phenomena: waves and particles. Briefly, particles are localised phenomena which transport both mass and energy as they move,
- while waves are de-localised phenomena (that is they are spread-out in space) which carry energy but no mass as they move.
- Physical objects that one can touch are particle-like phenomena (e.g. cricket balls), while ripples on a lake (for example).
- Such ideas led DeBroglie to the conclusion that all entities had both wave and particle aspects, and that different aspects were manifested by the entity according to what type of process it was undergoing.
- This became known as the Principle of Wave-Particle Duality.
- Furthermore, DeBroglie was able to relate the momentum of a “particle” to the wavelength (i.e. the peak-to-peak distance) of the corresponding “wave”.
- The DeBroglie relation tells us that p=h/lambda, where p is the particle’s momentum, lambda is its wavelength and h is Planck’s constant.
- Thus it is possible to calculate the quantum wavelength of a particle through knowledge of its momentum .
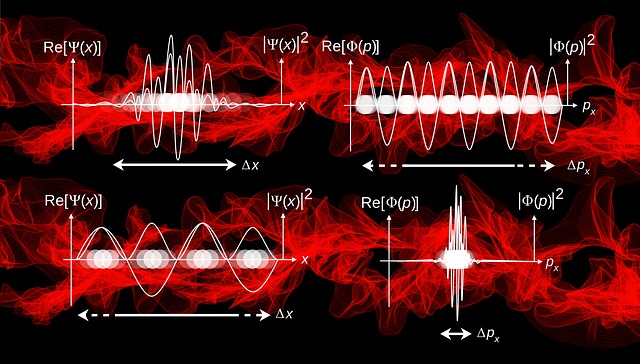
- In quantum mechanics electron is considered to be a wave.
- So it is very difficult to know the exact location of the electron in a wave packet.
- In 1927 the German physicist Werner Heisenberg proposed a principle which is known as uncertainity principle.
- Statement:-”The exact position and momentum of a particle can not be determined simultaneously with certanity.”
- Here I have tried to explain the complete quantum mechanics in a complete series of you tube videos, ( Link of playlist is enclosed here…)